Smart Grid Consumer Collaborative's State of the Consumer 2017
In a packed panel session co-located with Distributech 2017, on Monday, Jan. 30, a review of the Smart Grid Consumer Collaborative 2017 State of the Consumer report revealed key trends of interest for optimizing utility customer engagement programs.
The Consumer Symposium; "Beyond the Grid: Connecting Tomorrow's Consumers" highlighted the SGCC research, which was conducted as an online survey of 1,571 respondents from across the nation. It addressed four distinct technologies and services: Residential Solar, Community Solar, Green Power Plans, and Electric Vehicles.
Findings from the report will help utility personnel directly involved in consumer engagement programs as well as those concerned with how to best leverage business models associated with Smart Grid assets.
-
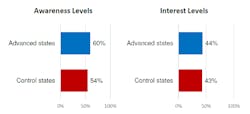
Key finding #1: Consumer smart grid technology awareness and interest levels are relatively uniform nationwide.
What it means: The survey cited differences between more advanced states vs. “control” states and found that “the policy environment, and the attendant level of technology in place to underpin new offerings, does not meaningfully impact either consumer awareness of or interest in Smart Grid technologies. Instead, it’s more about who you are and less about where you live.”
-
Key finding #2: Going beyond rooftop PV—consumers showed positive attitudes regarding community solar/shared solar and other “innovative acquisition models” which are emerging.
What it means: Utilities seeking flexibility in ownership models should be encouraged, because the survey showed that consumer interest in alternative acquisition models is strong — a key insight for smart grid stakeholders looking to increase adoption of these capital-intensive technologies. Certain smart grid-enabled offerings, such as solar, electric vehicles and smart appliances, require substantial initial investment. While consumers indicate growing interest in these technologies, a frequently stated barrier to adoption is these upfront costs. Fortunately, there are alternative acquisition models, such as leasing and power purchase agreements, that reduce or eliminate this upfront cost to the consumer. These include both direct and indirect monetization of consumer offerings, improving capital efficiencies and providing new areas for capital investments that earn a regulated return. -
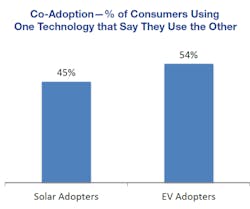
Key finding #3: The ongoing EV/PV co-adaption trend remains strong.
What it means: The projected growth for solar and EVs is robust due to a combination of market forces, including the rapid evolution of these technologies that promise to bring ever more competitive solar and EV offers to the consumer. Adoption of solar and EV technologies will have an impact on the consumer’s supply and demand relationship for energy, and this, in turn, has significant operational implications for utilities.
The SGCC “Consumer Driven Technologies” report’s Executive Summary for non-SGCC members is available at this link.