What Is the Right Way to Retrofit an IEC 61850 Smart Grid?
Retrofitting existing electrical grids with IEC 61850 smart grid technology is a cost-effective and practical alternative to implementing a smart power grid without rebuilding the entire network from scratch.
Despite the many advantages of the IEC 61850 standard, such as improved efficiency and resilience, retrofitting poses challenges like integrating legacy power systems into IEC 61850 networks and addressing security issues. Overcoming these challenges requires meticulous planning and adopting suitable tools and technologies, such as protocol gateways that streamline substation retrofits.
What Is a Smart Grid?
A smart grid is an advanced electrical grid that integrates various technologies to improve the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electricity services. This complex and vast system comprises multiple subsystems, including generation, transmission, distribution, and consumption—all interconnected through advanced communication and control technologies.
Smart grids use these technologies to monitor and manage electrical flows in real time, enabling the integration of renewable energy sources and improving the power grid’s overall resilience. One of the most significant trends in the evolution of smart grids is the adoption of the IEC 61850 protocol. This protocol is now widely accepted as the standard for energy systems, providing a comprehensive framework for communication and interoperability.
The Wide Adoption of IEC 61850
IEC 61850 differentiates itself from other energy protocols like DNP3 or IEC 101/104 by being specifically designed to meet the requirements of entire energy and power systems. Unlike other protocols that may focus on specific aspects, IEC 61850 provides an integrated standard that covers device configuration, data models, communication, and configuration management. This integrated approach ensures a more consistent and unified system design, which is critical for the efficient operation and management of modern power grids.
Recognizing the benefits of a unified protocol, countries worldwide are increasingly aligning their policies with IEC 61850 standards. As smart grids continue to evolve, integrating existing infrastructure with IEC 61850 becomes crucial.
Challenges of Integrating IEC 61850 Systems
Given the high costs involved in replacing all current infrastructure with IEC 61850-enabled systems, retrofitting existing grids has become the preferred method to maximize the value of current assets. However, connecting legacy power systems to IEC 61850 communication networks can be complex, as a variety of industrial protocols are used in field sites. Furthermore, bringing IEC 61850 devices into existing networks also raises serious security concerns.
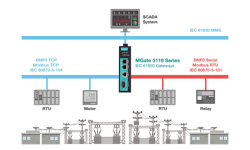
Challenge 1: Complex Protocols Can Be Overwhelming When retrofitting legacy power systems, you are likely to encounter many protocols, such as DNP3, IEC 101, and IEC 104, which are commonly used by SCADA or end devices. Sometimes, integrating Modbus PLC may be necessary. All these legacy intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) in the system need to be connected and managed simultaneously. Operators will not only face the challenge of protocol conversion but also the critical task of integrating all devices. Thus, the capabilities of IEC 61850 networks, including a unified protocol and policies, are crucial.
Challenge 2: Zero Tolerance for Downtime Critical power systems cannot afford any downtime. Therefore, protection against equipment failures, natural disasters, human errors, cyberattacks, and other external factors remains necessary. Operators at the field site may encounter device failure because of various factors like aging, insulation breakdown, mechanical problems, or overheating. External factors like lightning strikes or earthquakes can disrupt equipment and damage the network. In the event of unforeseen downtime, it is crucial to quickly identify the root cause and restore the network to its normal state.
Challenge 3: The Evolving Threat Landscape The frequency of cyberthreats in critical infrastructure environments is rising, with power substations being a prime target for malicious parties. Cracking a default password on a single network node is all it takes for a cyberattack. Once the network is breached, hackers can exploit your plain text configuration files and launch attacks or overwhelm your infrastructure with DDoS attacks. Hence, operators must remain vigilant of cybersecurity risks and prepare for worst-case scenarios using effective methods.
Protocol Gateways for Substation Retrofits
Modernizing a substation requires extensive resources and significant time and effort from a diverse group of professionals. Thus, simplifying substation retrofits, tackling common challenges with useful tools, and reducing cybersecurity risks are three crucial requirements to enhance power grid intelligence.
The key to addressing these three criteria is by choosing the right protocol gateway. To facilitate protocol conversion during substation retrofits, certain protocol gateways, such as the MGate IEC 61850 gateway, are specifically designed with these requirements in mind and incorporate multiple helpful features.
Quicker Settings: Legacy systems that need to be connected to IEC 61850 networks commonly use protocol communications, such as DNP3, IEC 101, IEC 104, and Modbus. Configuring IEC 61850 communications with multiple protocols can be very complex, especially when editing SCL files, which is a standardized file format used to ensure interoperability between devices from different vendors running different protocols. The MGate IEC 61850 gateways help you simplify the complex process by using the user-friendly SCL file generation function, reducing costs and effort associated with additional engineering tools and streamlining device configuration.
Minimal Downtime: In the event of communication errors, a rapid response is critical. The MGate IEC 61850 gateways are equipped with built-in diagnostic tools that quickly identify root causes. In addition, the Test Mode (IEC 61850-7-4) allows operators to simulate and test configurations before implementation, minimizing network downtime and ensuring continuous operation. Without the Test Mode, operators might have to spend a considerable amount of time manually disconnecting, reconfiguring, and reconnecting each node.
Secure Communication: Cybersecurity is paramount for substations. To enhance the cybersecurity of substation networks, the MGate IEC 61850 gateways incorporate communication protocol encryption by offering IEC 61850 MMS Communication Encryption (SSL) and adhering to the IEC 62443 and NERC CIP standards. Moreover, the MGate supports DDoS defense through its built-in detection capabilities, helping you detect abnormal packets and alert operators for an instant response. Finally, these IEC 61850 protocol gateways ensure the security of your configuration files by encrypting them during export.
With the advancement of smart grids and the widespread adoption of IEC 61850 standards, retrofitting existing substations has become crucial. Solutions like the MGate IEC 61850 protocol gateways are at the forefront of enabling this transformation, ensuring that legacy infrastructure seamlessly integrates with modern smart grid systems. By simplifying protocol conversion, prioritizing security, and offering user-friendly configuration tools, these gateways enable a more efficient, reliable, and future-ready energy infrastructure. As we continue to advance toward a smarter grid, embracing these technologies is essential to maximizing the value of existing assets and ensuring a smooth transition into the future of energy management.