Transformation of Global Electric Industry Depends on Energy Storage
In the concluding chapter for the World Energy Council’s World Energy Resources 2016 report, DNV GL asserts that energy storage is playing an increasingly crucial role in the transformation to a cleaner, smarter, safer energy future worldwide.
“Energy storage is pivotal to meeting the challenges facing economies worldwide,” says Paul Gardner, lead author. “With this chapter, which follows sections on a variety of generation resources and technologies, we hope to present the challenges and opportunities in energy storage with a thorough examination of the economic, regulatory and commercial factors surrounding it.”
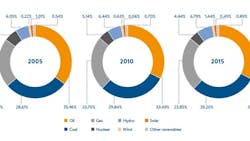
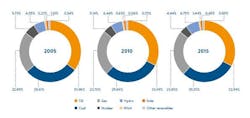
The chapter examines technical, financial, environmental and regulatory aspects of a variety of energy storage technologies including lithium-ion and flow batteries. It looks at the impact of increasing amounts of battery storage, and battery capacity in electric vehicles. Graphs depict storage technologies according to performance characteristics, using energy capacity and discharge time at rated power. Information gathered directly by PwC shows the levelised cost of storage in 2015 compared to the cost of 2030 in a bar graph, showing a projected decrease in future prices. The chapter develops three major conclusions:
- The main areas of growth in the next five years are likely to be in small-scale battery storage in conjunction with solar PV; in utility-scale electricity storage; in electric vehicles; in commercial, communications and software capabilities to allow DER to be aggregated, in a ‘virtual power plant’ or ‘swarm’; in pumped storage hydro; and in islanded use cases integrating renewables.
- Most commercial interest is in battery storage and the costs of several storage technologies will fall as production volumes increase.
- The future outlook for energy storage markets is good due to an increasing need, but the regulatory and legal frameworks are failing to keep pace.
According to the World Energy Council, the investment community has good reason to be excited about the innovation and business models that will emerge from new opportunities. With the cost of capturing and storing wind and solar energy coming down, its deployment across the world will increase.
The World Energy Council is the principal impartial network of leaders and practitioners promoting an affordable, stable and environmentally sensitive energy system for the greatest benefit of all.
Lead author Gardner produced the chapter with collaboration and contributions from a strong working group of experts from across the energy industries. Gardner is an electrical engineer who has worked in the renewable energy industries, principally wind, since 1984. His experience includes wind turbine electrical systems, network connections, grid integration issues, and strategic and market advice to government bodies, NGOs, established companies in the renewables industries, and new entrants. DNV GL’s active team of energy storage analysts, who provide technical and commercial advice to clients on storage technologies, also played a large role in the development of the chapter. World-class energy storage testing labs and certification activities provide DNV GL with the ability to guide organizations across the entire energy storage value chain.