The Zhoushan Islands are a critical and rapidly developing area situated 18.27 km (11.35 miles) off the southeast coast of China. The reliability of supply to the islands was inadequate, resulting in power failures due to the high load demand and the weak power system. In addition, this area is subject to typhoons and other natural disasters that often caused a total power outage of the 110-kV grid because there was no backup. The successful commissioning of the voltage source converter high-voltage, direct-current (VSC-HVDC) project now not only interconnects the islands with the China transmission system, but also provides reactive power compensation and stabilizes the island grid.
The Zhoushan Islands
The Zhoushan Islands are located in the Hangzhou Bay and include five islands: Dinghai, Daishan, Qushan, Yangshan and Sijiao. The islands cover a total geographical area of 1440 sq km (556 sq miles) with a population of 1.173 million. In 2012, total installed generation capacity was 765 MW, and peak load demand of the Zhoushan was 818 MW. It is estimated that the peak power demand will increase to 2649 MW by 2020 and 4775 MW by 2030. This steep load growth is due to increased industry and coastline development.
Prior to installation of VSC-HVDC, there were two 220-kV and three 110-kV circuits to Zhoushan Islands from the Shanghai and Ningbo power grids on the mainland. Between the islands of Dinghai and Daishan, there were two interconnections: a 220-kV and 110-kV submarine cable transmission. There was only one 110-kV submarine cable linking the remaining three islands. All the existing mainland and inter-island interconnections were high-voltage alternating-current (HVAC) circuits.
The weak interconnection and unavailability of large sources of generation within islands made the Zhoushan grid system highly unreliable, unstable and dependent on small generation plants. Therefore, the Zhoushan grid system required reinforcement.
Alternative Schemes
Two possible alternative solutions were considered to install the new supply channels to the existing Zhoushan Islands transmission system: HVAC or VSC-HVDC. Following a detailed study of the technical and economic aspects of the two alternatives, VSC-HVDC was chosen as the final solution. The major factors that led to this decision were many.
Voltage Rise of AC Cables
The charging current required by AC cables causes a voltage rise at the terminals. The Zhoushan Island grid system submarine cables already create this voltage problem. It would worsen if new AC transmission cables were added. This problem would not occur with the VSC-HVDC option.
Compensation to Impact Load
There are many large ports located on Zhoushan Islands that are subject to impact loads arising from the cranes loading and unloading containers. This creates a negative impact on an AC grid, causing voltage fluctuations and a low power factor. The situation is even more serious on the islands of Yangshan and Sijiao because of the relatively low load capabilities of these two small grid systems. The VSC-HVDC system offers a self-integrated power compensation function.
Wind Energy Integration
Being rich in renewable energy makes the Zhoushan archipelago a potential location for the installation of wind farms. According to recent wind power development plans for Zhoushan City, the wind power installed capacity is expected to reach 1850 MW by 2020, but because of unavailability of an efficient transmission system, it will not be possible to connect the total wind power generated to the existing AC grid. The VSC-HVDC solution offers superior functionality in terms of integrated voltage regulation, power-quality coupling control and integrated frequency control.
Control and Stability
The critical geographical location and low power ratio of mainland interconnection makes Zhoushan Island a weak and poor load-sharing grid system. Compared to that existing system, instantaneous power flow change and adjustment control of the power capacity function makes the VSC-HVDC solution superior to HVAC.
VSC-HVDC offers independent control over active and reactive power and dynamic response, as STATCOM keeps the power system stable. Because of its rapid and multi-target control, it automatically realizes the optimization and activates emergency actions by isolating faults.
Black-Start Function
The VSC-HVDC option has a distinct advantage by being able to offer the black-start function. In the event of a total blackout of the Zhoushan grid system, the black-start function can be used to restore power. This process is designed so that the Yangshan converter station will charge the Yangshan 110-kV AC system, the Yangshan converter station will transmit power to Daishan converter station and start the generators on Daishan Island.
Control Strategy and Operation
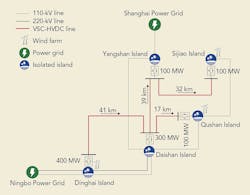
The Zhoushan project is mainly based on the symmetrical monopole topology where the radial network establishes the Daishan Island as the centralized control center. All the island converter stations are similar in design. The control strategy was designed by the Zhejiang Electric Power Co. together with NR Electric, which manufactured and supplied the control, protection and SCADA systems.
The DC voltage deviation control for multi-terminal converter stations has been adopted. It sets one station as the master to control DC voltage and automatically balances the active power among stations; other stations are also able to set DC voltage control. Their voltage setting has a deviation in proper order to compare with the master station. This strategy ensures the DC voltage of the whole system is controllable and only controlled by the designated converter station. If the master station is out of operation, the one with the smallest voltage deviation takes over as the master station to keep the remaining system in normal operation.
In this project, there are communications channels between the islands, but even when these communications channels are interrupted, the voltage deviation control strategy can still maintain stable operation of the system.
With operation in five-terminal mode, the Dinghai converter station, which has the largest capacity and strongest power balancing ability, is set to be the master DC voltage control station. The Daishan converter station serves as the backup and can take over voltage control if the Dinghai converter station fails.
HVDC Protection and Operation
A key factor required to maintain the VSC-HVDC’s efficient output is the protection system, which plays an important role. Ranging from the valve side of the connecting transformer to the DC cable, the whole protection system keeps track of its instrumentation for convenient and error-free operation. Taking valve protection as an example, there is over-current protection and overvoltage protection. When the protection acts, it blocks and trips the AC incomer and opens the DC disconnectors, shutting down the connecting transformers.
The main purpose of the Zhoushan project is to provide a stable grid system with an ever-increasing load-transfer capability and enhanced reliability of the complete Zhoushan grid system. Moreover, the multi-terminal VSC-HVDC scheme has the capacity to carry an enormous amount of power through various operational modes. To improve the operating flexibility and maximize the advantages of multi-terminal VSC-HVDC, several operating modes can be executed according to system demand. Zhejiang Electric Power Co. worked together with NR Electric to confirm all components (for example, control and protection systems, IGBT valves and valve-based control) to ensure smooth operation in every mode.
The main operation mode of the VSC-HVDC project under normal operating conditions is for the Dinghai converter station to act as the sending end and the other four converter stations to operate as the receiving ends. When the Dinghai converter station quits operating, the Daishan will act as a sending end, and the other three converter stations will operate as the receiving ends. The project has a total of 26 operational modes that represent various combinations of islands in and out of the grid. In addition to the multi-mode operational advantages, VSC-HVDC also offers the following features:
- Offers long-distance bulk power transmission
- Enhances power stability of multi-HVDC feed-in areas
- Includes city center in-feeds
- Provides HVAC grid interconnection
- Creates reasonable grid system short-circuit levels
- Establishes a ring network using a back-to-back VSC-HVDC that limits short-circuit capacity.
Zhoushan Project Results
The Zhoushan project commenced in March 2013 with the installation of the 129 km (80 miles) ±200-kV DC submarine power cable and 11 km (6.8 miles) of 200-kV transmission line. The project, witnessed by representatives of the State Grid Corporation of China, was commissioned on July 4, 2014. Currently, the project is operating in a five-terminal mode using the Dinghai converter station as its main DC voltage control station effectively transmitting power to the other four islands. To date, several principal advantages of this successful VSC-HVDC scheme have been recorded:
- It has increased the power supply and enhanced reliability of the grid system, especially the grid systems on the northern islands.
- The increased voltage support for the existing ±50-kV 60-MW LCC [line-commutated converter]-HVDC system on Sijiao Island provides maximum output without commutation failure.
- The improved power quality provided by the reactive power compensation function. This is especially important on Yangshan and Sijiao inlands, where the grid system experiences the impact loads attributable to cargo handling at the ports.
- By mid October 2014, VSC-HVDC had provided 15.1 million kWh to the Zhoushan grid, in addition to transmitting 5.14 million kWh from the wind farms.
- Finally, this VSC-HVDC project operated normally and adequately in squally weather when Typhoon Nakri occurred in July 2014.
The Zhoushan Island grid is more stable, reliable and has sufficient capacity power to provide a flexible power transmission system. This VSC-HVDC project has increased the availability of the power supply significantly and enhanced the power quality on the Zhoushan Islands.
The State Grid Corporation of China is now operating the world’s first five-terminal VSC-HVDC system, the Zhoushan Island transmission system. This project, a ±200-kV HVDC scheme with a capacity up to 1000 MW, is a successful example of using well-engineered, cutting-edge technology to establish a highly reliable HVDC power supply.
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank the NR Electric Co. for its technical support and assistance with this major project.
About the Author
Yingyi Li
Yingyi Li is head of the dispatching and control center in Zhejiang Electric Power Co. He has a MSEE degree from Zhejiang University and has been working in the energy sector since 1994.