High-Voltage Breakers Get a Health Assessment
Rochester Gas & Electric (RG&E), a subsidiary of Iberdrola USA, requires an extremely reliable infrastructure to provide electricity to more than 367,000 customers and gas to more than 303,000 customers, all from nine counties around Rochester, New York, U.S. In addition, limited operation and maintenance budgets influence maintenance intervals, which, ultimately, affect overall asset reliability.
Of particular importance is a cross-state 345-kV line connecting RG&E to New York Power Authority. To enhance the reliability of that transmission corridor, RG&E sought to equip its type PMI (gas-pressure-interrupter, multiple-tank, independent pole-operated) capacitor bank breakers with real-time remote condition monitoring. With the latest monitoring technology, RG&E was able to institute proactive, rather than reactive, maintenance practices.
RG&E wanted to record all trip and close operations, as well as the timing statistics, of these highly critical circuit breakers. In addition, RG&E had limited to no Ethernet communications at remote substations, which posed a major challenge. The fleet of breakers RG&E wanted to increase the reliability of included 121-kV and 362-kV type PMI sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) capacitor bank breakers.
Monitoring
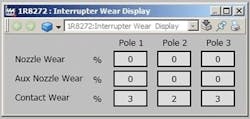
By installing equipment monitoring packages directly connected to the circuit breaker, myriad breaker statuses and performance parameters can be determined. The required device and sensors are capable of monitoring the interrupter wear, SF6 gas integrity, leakage rate, mechanical integrity of the entire breaker, trip/close conditions, mechanism charging system and the control cabinet heating system. Examples of issues the monitoring device is capable of detecting include a long reaction time for one or all of the poles, fault current interruption with a subsequent increase in calculated interrupter wear and slow SF6 gas-leak detection.
By measuring specific areas of the breaker, the monitoring system alerts RG&E to conditions that may compromise the operation of the breaker before a failure occurs. With the utility being advised when maintenance is required, RG&E no longer needs to perform time- or use-based maintenance.
Time-based maintenance is performed every 10 years regardless of the load the breaker has handled or the number of times the breaker has switched in and out of the line. Use-based maintenance is performed after a certain number of switching operations has occurred at a particular current load. For example, an overhaul may be performed after six switches at 63 kA or 10,000 switches at 3 kA. In condition-based maintenance, a service crew is only sent to the site when a warning alarm states that the breaker requires maintenance of some kind. Performing condition-based maintenance will eliminate unnecessary downtime and save money on unnecessary overhauls.
With condition-based maintenance, repairmen arrive at the substation fully prepared with all parts and equipment because they completely understand the issue. Fully understanding the problem ahead of time also minimizes the in-field repair time because diagnostics can be performed prior to mobilization of the service engineers. Prioritization of the needed repairs will further reduce outages, maintenance times and costs.
The monitoring device also helps RG&E to be more environmentally friendly. With early leak detection, the leak is repaired much more rapidly, which releases less SF6 into the atmosphere. SF6 is a greenhouse gas that is 22,800 times stronger than carbon dioxide. RG&E also reduces cost on SF6 gas purchases by minimizing the amount of gas that needs to be replaced in a leaking breaker.
Installation and Setup
The equipment monitoring packages were installed in the control cabinet of each circuit breaker. RG&E chose to use ABB’s Circuit Breaker Sentinel monitoring device because of the features and capabilities it offers. Devices were installed on either a wall panel or a floor-mount bracket, depending on space availability within the control cabinet. The unit consists of a microprocessor and sensors used to collect the required breaker information and then are connected to the microprocessor by pluggable connections.
Once the wiring and installation were completed, the setup, or the parameters, had to be set. The setup was performed in less than five minutes, because the device was set automatically to default parameters once the breaker and mechanism type were selected. The parameters also are multi-staged. Not only was a normal operation range defined, but caution and problem limits were set, as well. Alarms notify RG&E when a certain condition, such as coil energization time, reaction time, contact speed, mechanism times, interrupter travel time, SF6 pressure and temperature, and interrupter wear increments, reach the caution or problem limit. During each data collection performed by the monitoring device, the numeric value of the condition and distance to the alarm limits are collected, transmitted and stored.
Communication
RG&E determined that wireless communication would be the most cost-effective means of communications. The monitoring system will securely furnish periodic reports and maintenance recommendations to a central location to be reviewed. If needed, the same communication system can automatically dispatch expert service personnel to address any site assets whose needs are remotely detected.
Any communication using the transmission line power system needs to meet the North American Electric Reliability Corp.’s (NERC’s) Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) compliance. NERC’s CIP plan comprises more than 100 reliability standards and sets requirements for protecting critical assets, those that materially impact the reliability of the transmission line power system. In this case, the wireless communication functions independently from the utility’s transmission line operating and control system, exempting it from NERC’s CIP requirements.
Reliability Optimized
While evaluating suppliers for the transmission line reliability upgrade project, RG&E attended the Finepoint Circuit Breaker Conference in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, U.S. During the conference, the utility was introduced to ABB’s asset monitoring solutions and quickly realized the benefits of using the company’s in-house technology for software integration.
ABB’s Asset Optimization software package is designed to specifically monitor customer assets regardless of type. It allows all information to be examined in one seamless interface by using object-oriented features. This interface allows a complete view of each circuit breaker’s health and history. It also displays all information required to install, operate and maintain each breaker, including documentation, alarms, events, notifications, real-time camera feed, reports, weather conditions and integration with maintenance management systems.
The software package helps RG&E to process information in a way that optimizes cost savings, as well. It maximizes RG&E’s maintenance effectiveness using root-cause analysis. It does this by assisting circuit breaker problem diagnoses as well as offering corrective recommendations. For example, by calculating historical trends of the particular condition, the system can identify whether this is a sudden or gradual change to the condition value. Additionally, the system redundantly archives the data to ensure reliable long-term storage.
With multiple monitoring devices on several breakers, the interface also can cross-examine all features among the power equipment. This way, the software can prioritize and better troubleshoot all problems within the substation, line or fleet. The highly scalable system also can be readily applied to other systems and electrical apparatuses, and can accommodate
future growth.
Increased Reliability and Decreased Maintenance
CIGRÉ conducted a reliability study that showed most failures occur in the main insulation to earth, followed by compressors and pumps, control elements and the interrupting unit. The monitoring devices focus on all of these areas, ensuring increased reliability. On the other hand, the greatest maintenance savings can be expected through comprehensive on-line monitoring of breaker timing, which is also monitored by the device.
Additionally, RG&E was able to secure funding assistance through a recent public utility commission-granted rate increase, intended for reliability improvements, to acquire the turnkey engineering and installation support necessary to achieve these goals.
Wireless monitoring devices render reactive maintenance no longer necessary. Proactive maintenance is required; however, it is much less costly. Additionally, much more information is known about the issue the breaker is experiencing, which means it can be repaired in significantly less time. This is very important because, with time, operation and maintenance resources and experience continue to decline, reducing the efficacy of corrective and preventive maintenance services.
This monitoring solution monitors the interrupter wear, SF6 gas integrity and leakage rate, mechanical integrity of the entire breaker, trip/close conditions, mechanism charging system and control cabinet heating system. The customized software package allows the health and history of each breaker to be examined in one seamless interface. If more than one monitoring device is linked to the interface, the breakers may be cross-examined. In summary, real-time wireless monitoring provided RG&E with decreased maintenance costs and increased reliability.
Edward Messmer([email protected]) is the supervisor of substation and recloser automation at Rochester Gas & Electric. Since joining RG&E in 1981 as a meter reader, he has worked in the electric substations department, in the field operations division, as a electrician’s helper, substation maintenance and a tester, performing Doble testing and equipment repairs. He also served as substation foreman before being promoted to substation maintenance engineering in 2003.