Modernizing and Securing the Grid During COVID-19
Electric grid management is an integral component of the quality of service customers receive. With the advancement of new technologies to meet the rising needs of customer expectations, electric utilities like Public Service Electric and Gas Co. (PSE&G), part of Public Service Enterprise Group, are incorporating microgrids into their existing distribution systems to meet the rising needs of customer expectations. With the implementation of distributed generation, utilities will experience lower distribution losses, differed capital expenditures and reduced maintenance costs. At the same time, consumers will gain greater control over the energy costs, including generating their own power, while realizing the benefits of a more reliable energy supply.
Multiple components are required to provide benefits to customers and manage the complete advanced distribution management system. Distribution SCADA (D-SCADA) is the fundamental component to decrease customer interruption duration with intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) and reliable communication. The D-SCADA system uses architecture of interconnected IEDs to report abnormalities and allows remote control. It is a critical system, used by electric operations and planning teams to minimize the customer minutes of interruption (CMI) by allowing real-time remote monitoring of the electric distribution grid. D-SCADA reduces the length of outages, improves reliability of IEEE 1366 indices and increases safety of both PSEG employees and the public.
When combined with the Geographical Information System (GIS), it uses spatial locations, layers of information and the visualization of custom maps to reflect actual field conditions of electric distribution circuits and devices to provide an as-operated grid model.
Both systems serve as a smart grid platform to further enhance and supply information to the next generation of distributed management system (DMS), outage management systems (OMS), distributed energy resource management systems (DERMS), and many more systems. Now, operations’ approach can began to shift from reactive to proactive.
PSE&G deployed technology-enabled workers throughout its territory to work through the global pandemic. The data received from these devices enabled the utility to monitor field conditions and quickly respond to system abnormalities in substations and outside plant assets. By combining various monitoring tools, the operations team can now diagnose a problem rapidly and deploy the solution.
Grid Modernization
The Energy Strong II is a US$824-million investment program to strengthen PSE&G’s electric and gas systems, improve reliability and enhance resiliency. A subcomponent of the program, grid modernization has entailed improving communication to remote field devices and providing real-time data collection using 4G technology. Construction began in late 2019 and key project activities took place during the COVID-19 pandemic to successfully deploy wireless communication and commission assets to D-SCADA. In scope, 2600 devices — communicating by telephone lines in the D-SCADA system — will be retrofitted with wireless communications by the end of 2022. These devices include 4-kV, 13-kV and 26-kV reclosers and substation remote terminal units (RTUs).
In addition, as part of the Energy Strong II program, the DSCADA team has installed nearly 1800 reclosers in the D-SCADA system. The addition of these devices has increased reliability for more than 2.3 million customers in the PSE&G service territory by further sectionalizing electric distribution circuits, resulting in fewer customers experiencing power outages.
Using 4G wireless communication will result in operation and maintenance (O&M) savings of an estimated US$500,000 over three years. PSE&G’s original troubleshooting process involved submitting a request ticket to a third-party vendor and waiting multiple days for the vendor to survey and fix the problem. This time frame was not ideal in the 24/7/365 operating environment. Deploying wireless routers enables the team to identify an issue quickly and work with internal stakeholders on an efficient resolution.
Now the system operates with real-time data as a result of enhanced communication, providing a point-to-point connection that goes directly from the end device to the central server. With reliable information available to PSE&G in real time, data is modeled to understand the status of distribution circuits for load monitoring purposes.
Safeguarding Substations
An electric substation is a highly critical asset to a utility, making it a possible target for cybercriminals. Assets such as wireless RTUs can be attacked, causing damage and malfunction within the distribution grid. Cyber threats have been on the rise globally, and with the ever-growing implementation of new technologies, utilities must strengthen the security of the modern substation.
PSE&G is implementing new technology by deploying an Ethernet Security Gateway — which adds additional layers of security — and by migrating the existing IEDs into a single substation encrypted and dedicated network. This involves migrating the utility’s existing 18,000 IEDs into a single-substation encrypted and dedicated network. This technology is being implemented at over 280 substations to secure existing relays and local area networks (LAN). This process provides security to our assets, device management and tracks activity to eliminate unauthorized access.
This solution authenticates users accessing the protected network against active directory, authorizes which devices users may access (user roles), and provides accountability by logging access and actions (syslog). PSE&G implemented redundancy in its password management system with load balancers and high-availability servers to provide uninterrupted, continuous access. Its configuration and design are unique and strictly aligned for utility asset protection. The load balancer provides authentication of the user while the server collects data from the different devices in a substation and stores it in a centralized database for easy access. This means if one server fails, the system will failover to a secondary database, enabling 24/7 availability of the database.
This solution supports securing engineering access and NERC Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) compliance standards for IED password management by eliminating unmanaged system accounts. The logs retrieved from the servers help the engineer to understand the root cause and maintain a trail of records for compliance and audit purposes.
COVID-19 Impact
PSE&G is constantly prepared for unexpected events, maintaining contingency plans to respond to emergencies to defend critical infrastructure and ensure the most reliable electric service to customers. With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, like many utilities worldwide, PSE&G was faced with new challenges and variables, so it had to adapt. Its business continuity plans were constantly evolving to manage a dynamic workforce. The utility’s highest priority was the safety of its workforce and customers. The D-SCADA team continued business as usual, transitioning to a hybrid environment, quickly complied with COVID protocols and limited face-to-face contact. This was a must as key initiatives were beginning to take off with SCADA (like for the Energy Strong II program), new technology deployments to support cybersecurity standards and many other capital substation projects.
While embarking on these new initiatives, approximately twenty new hires supporting the D-SCADA and GIS systems started immediately prior to or during the pandemic. The size of the team tripled in a few months. This involved hiring engineers and conducting onboarding activities virtually. With a hybrid schedule in place, team members were cross trained on-site, with limited interaction, and ensured transparency with how we conducted essential business virtually. A strong team was assembled with mixed, diverse skills, and encouraged to succeed with meeting project milestones that included aggressive deadlines.
In addition to working in a pandemic setting, the PSE&G service territory experienced numerous inclement weather events, with the most significant events being Tropical Storm Isaias in August 2020 and Hurricane Ida in September 2021. Tropical Storm Isaias ranked one of the worst for power outages in New Jersey. Over 575,000 homes and businesses lost power across PSE&G service territory. The importance of D-SCADA remote IEDs was imperative in the reduction of customer interruption duration. Isaias also led to over 7,800 breaker operations and more than 1,100 breaker lockouts, which required circuit patrols. Electric Operations issued over 8,500 remote SCADA controls, to restore customers and set circuits up for work to keep workers safe. With changing priorities and unknown risks, project milestones have been continuously met, as PSEG sees rapid asset and technology growth.
Investment Benefits
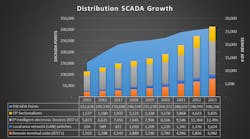
D-SCADA growth is necessary for the implementation of advanced technologies. On completion of the current proposed projects and filings, D-SCADA is estimated to grow exponentially by 2024, to over 308,000 points. This increase will provide monitoring of critical assets, remote operation and data for analytical business improvement processes. Operation and maintenance costs will progressively decrease with the advancement of assets, their functionality and integration with D-SCADA.
Spatial intelligence enables organizations to connect data with geography. The cost of asset maintenance declines sharply once exact equipment is recorded with precise information. As weather patterns and conditions become more unpredictable, the ability to provide quick and detailed data becomes the first step to reduce customer service interruptions. Location-based knowledge can only come from a GIS to support restoration.
The following benefits can be realized:
1. Remote control
• No truck rolls
• Avoid exposure to hazardous travel conditions
2. Quicker restoration time
• Geographic and schematic views reduce the risk of
invalid or suboptimal switching sequences
• Fault location, isolation and supply restoration (FLISR)
provides intelligent and rapid prediction/identification
of fault location, isolation of fault section, and
restoration of supply to all un-isolated (healthy) parts
of the network while the damaged area is repaired
3. Lockout condition identification
4. Real-time condition alarming
5. Job tracking for abnormal loops
6. Real-time view of 69-kV and 26-kV one-lines
7. Prioritization of restoration
8. Power flow monitoring
• Proactive approach to switching overloaded
transformers and circuits once the 90% threshold is met
9. Validation of switching
• Prevent network overload conditions, voltage
instability, and potential issues with crew personnel
and network equipment
• Validation managed with simulation as well as what-if
simulation for short- and long-term planned work
10. Advanced analysis engine for predicting and identifying incident locations based on event analysis from SCADA devices, customer calls, damage assessments, overload conditions, etc.
• Analysis of additional data points results in more
accurate analysis, thus shorter restoration times
11. Readily available reports for quick analysis, including loop loads, heaviest loaded circuits and transformers.
PSE&G is advancing its culture to implement and use current generation automation systems to improve electric operations safety, efficiency and sustainability in power delivery. By building a resilient, digital and fully integrated power grid management provides efficient alternatives to reduce the frequency of customer interruption. D-SCADA is the bedrock for proactive grid management, enabling PSE&G to meet customer demand with higher reliability and resiliency. Providing cleaner, renewable energy while managing a multitude of data and dynamic energy flow is a tremendous success for all stakeholders — PSE&G and its strategic partners, regulators, policy makers, governments, consumer advocates and many others.
MASROOR KHAN is a principal technology product consultant — Grid Engineering & Commissioning at PSEG in the Utility Technologies group. She is responsible for providing technical and project management support on various electric D-SCADA initiatives. Her project portfolio includes multimillion-dollar technology projects to enhance communication, which allow for real-time monitoring and remote control of the electric distribution grid. This includes PSEG’s Energy Strong II program, which aims to enhance reliability by deploying over 3,000 smart devices to the grid. Khan has a BS in Civil Engineering and a MS in Engineering Management from New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT).
LUKASZ KUBAS is the technology group product manager — Grid Engineering & Commissioning at PSEG in the Utility Technologies group. He oversees substation engineering and commissioning of IED’s across the entire service territory into a centralized D-SCADA system. Kubas’ team is responsible for the maintenance of over 18,000 IEDs in the current portfolio across all substation and remote locations. Through real-time data acquisition, he pioneered preventive tools to enhance monitoring within electric substation. He focuses on automation, safety, and reliability of the electric grid by utilizing technology. He has 15+ years of experience in project implementation, operations, asset management, and data analytics. Kubas graduated with his MBA in Project Management and holds a BS in Technology Management.
About the Author
Masroor Khan
Masroor Khan is an engineer within the Electric Asset Strategy group at PSE&G. Her responsibilities include maintaining the Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) and contributing to smart grid technology. This includes creating numerous data points, analytics, notifications, and visual displays in CMMS from various sources that include transformer monitoring equipment, gas density monitoring equipment, and SCADA. Other responsibilities include condition-based maintenance, building interfaces in CMMS, and asset health scoring. Masroor has a BS in civil engineering and a MS in engineering management from New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT).
Lukasz Kubas
Public Service Enterprise Group